
FaceTime Like a Pro
Get our exclusive Ultimate FaceTime Guide 📚 — absolutely FREE when you sign up for our newsletter below.

FaceTime Like a Pro
Get our exclusive Ultimate FaceTime Guide 📚 — absolutely FREE when you sign up for our newsletter below.
Explore the complete history of iOS, from the original iPhone OS 1 to iOS 26—key features, design changes, and Apple’s biggest software milestones.
Since its debut in 2007 alongside the first iPhone, iOS has come a long way. Each new version has brought fresh features, design changes, and performance improvements. iPhone OS 2 brought the App Store, while iOS 14 incorporated 5G connectivity, iOS 18 introduced Apple Intelligence features, and iOS 26 offered a new Liquid Glass design.
In this editorial, we will revisit history and discuss different versions of iOS, from the initial iPhone OS to the recently launched iOS 26. You will learn about the key updates of various versions and the turning points in the evolution of the iOS operating system.

Apple unveiled iOS 26 during WWDC 2025 on June 9, marking a significant shift in the iPhone’s software journey. It introduced a bold redesign and a new naming convention—aligning the version number with the calendar year of intended use (2026). This change brought uniformity across all Apple platforms, including macOS, iPadOS, watchOS, and tvOS.
The standout feature of iOS 26 is the Liquid Glass design language, inspired by visionOS. This aesthetic replaces the long-standing flat design introduced in iOS 7 with translucent, curved, and refractive UI elements that feel more fluid and immersive. Apps like Camera, Photos, Messages, and Phone received major interface upgrades, creating a more cohesive user experience.
Apple also supercharged its Apple Intelligence suite. With improvements to Visual Intelligence, Image Playground, and Shortcuts, iOS 26 introduced new capabilities like Live Translation, Call Screening, and DJ-style Audio Mix. Even CarPlay saw enhancements, with support for Live Activities and Tapbacks.
Apple released the developer beta of iOS 26 on June 9, 2025, followed by the public beta in July. The full version rolled out in September alongside the launch of the iPhone 17 series.
Key Features of iOS 26
Apple gave iPhone users a preview of iOS 18 at WWDC 2024 and officially launched it on September 16, 2024, along with the iPhone 16 series. This major update significantly boosts personalization options across the system and apps. You can customize the Home Screen layout and change the app icon theme.
Additionally, the Control Center can be customized to accommodate new quick controls. For advanced privacy, iOS 18 allows users to lock apps and select which apps can access specific contacts.
The native apps, especially the Photos, Notes, and Mail apps, also received a major overhaul. Further, the company introduced a powerful AI-powered feature called Apple Intelligence. Last but not least, the iOS 18 Accessibility features make it easier to navigate the iPhone.
Key features of iOS 18

iOS 17 was announced at WWDC 2023. The focus of iOS 17 was on redesigning and upgrading the system apps and features. The Message, FaceTime, and Phone apps have several enhancements. Additionally, Apple enhanced connectivity by introducing NameDrop and FaceTime on Apple TV.
The most highlighted features of iOS 17:
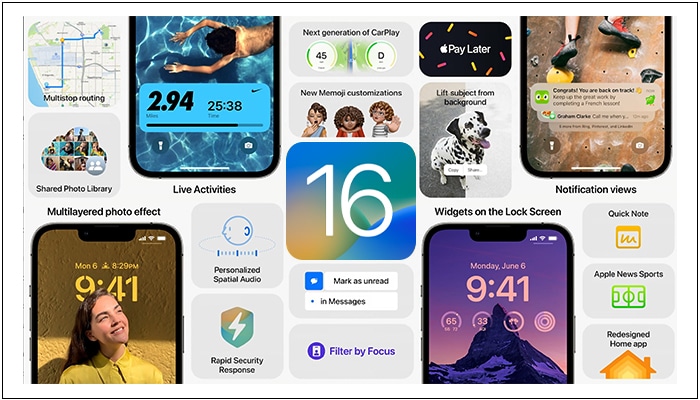
iOS 16 was announced at the WWDC event in June 2022 and released in September 2022.
The most noticeable upgrade in iOS 16 was the addition of supported features for the Dynamic Island on iPhone 14 Pro models. It made the new notch design more fun by displaying animated notifications and offering controls around the camera.
Also, Crash Detection, Always-on display, Emergency SOS via Satellite, and other exclusive features of the iPhone 14 series are supported with iOS 16.
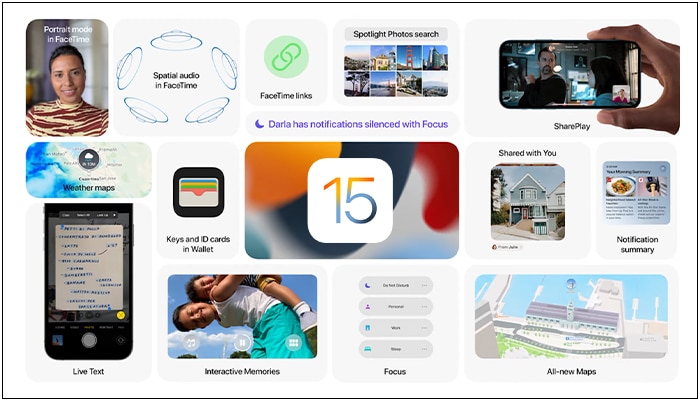
Unlike iOS 16, the iOS 15 update focused more on software bug fixes, system improvements, and refining the features of built-in apps.
Additionally, the pandemic era influenced the introduction of these feature upgrades. Apple focused on enhancing security and privacy, preventing ad tracking, and improving Siri, Camera, FaceTime, Messages, and other features.
As of writing, iOS 15 is supported on the iPhone 6S series and later, as well as the iPod touch 7th generation.

The iOS 14 version lists similar system improvements, very much like iOS 15. There were no significant changes. Apple added several enhancements, including privacy controls, Home Screen widgets, and customization options.
Key features of iOS 14:
Before iOS 13, iPad also ran iOS. However, Apple took a significant step by introducing a new iPadOS, designed to make the iPad more productive and potentially serve as a laptop replacement. Since then, iOS and iPad OS have always been rolled out simultaneously.
The most noticeable new feature was the introduction of Dark Mode. Additionally, iOS 13 improved essential functions, such as faster app start-up, Face ID, Portrait Lighting, and the redesign of pre-installed apps.
Key features of iOS 13:
The 12th iteration of the iPhone software had just a few new additions. Primarily, it improved regularly used functionality for providing a better user experience. Apple introduced Siri Shortcuts, ARKit 2, Screen Time tracking, etc.
Key features of iOS 12:
iOS 11 has special features to support the iPod touch, iPad, Apple Watch, and Apple TV.
Therefore, its primary features included more iPad-specific features, such as split-screen apps, drag-and-drop functionality, a file browser app, and support for Apple Pencil handwriting.
Key features of iOS 11:
The release of iOS 10 was a watershed moment for the Apple ecosystem. It offered several APIs to integrate third-party solutions into the system apps. Thus, the iPhone gained a boost in interoperability and customization through its UI and applications. Additionally, Siri has become more accessible to third-party apps. The best part was that Apple allowed users to uninstall built-in apps.
Key features of iOS 10:
iOS 9 prioritized building a solid base for the operating system to improve the speed, responsiveness, stability, and performance of older devices. After significant modifications to iOS’s design and technological base, users started to feel that iOS was no longer the reliable, trustworthy, and competent it had previously been.
So, Apple decided to focus on strengthening the OS’s foundation rather than introducing new features, laying the groundwork for the larger enhancements in the next iOS updates. To garner public reaction and acceptance, iOS introduced the Public Beta feature. So, before the actual release of the upcoming iOS version update, people can get a taste of it.
Key features of iOS 9:
In iOS history, iOS 8 was a significant update as it introduced the contactless payment system Apple Pay and the Apple Music subscription service. It also polished the iCloud features for more reliable and consistent performance. The most useful feature unveiled was the Handoff feature, which allows for seamless switching between Apple devices.
Apple walked in with a Dropbox-like iCloud Drive and the addition of an iCloud Picture Library and an iCloud Music Library. To save subscription costs, Apple offered Family Sharing, which allows users to enjoy content individually with a single subscription. Moreover, the HealthKit and HomeKit features focused on users’ daily lives.
Key features of iOS 8:
Family SharingiOS 7 was a troublesome update, and users were dissatisfied as things didn’t operate as expected. The update included a significant redesign of the user interface, opting for a flat look. However, some users found it difficult to read due to the tiny, thin letters, and others experienced motion sickness from the constant animations.
Additionally, Apple provided quick access to the most frequently used features through Control Center and introduced AirDrop, Activation Lock, and CarPlay. Additionally, Siri got new voices and a redesigned look.
Key features of iOS 8:
In the history of iOS versions, iOS 6 saw the most controversy due to Apple’s escalating rivalry with Google. Although the newly launched Siri was a significant breakthrough in technology, issues with it led to substantial revisions.
Besides, from iPhone OS version 1.0, Google has included the Maps and YouTube applications pre-installed. But this time, Apple replaced Google Maps with a new Apple Maps. It fell short due to glitches, inaccurate instructions, and issues with other functionalities.
Sidelining the flaws, iOS 6 features a Podcast app, a more capable Siri, a Panoramic mode in the Camera, and the ability to make FaceTime calls over cellular data.
Key features of iOS 6:
iOS 5 was a turning point for Apple, as it introduced crucial new features, including Siri, iCloud, wireless iPhone activation, and Wi-Fi iTunes syncing. Users could download and install software updates on their iPhones without a computer. Additionally, for a better user experience and accessibility, the iPhone features Notification Center and iMessage.
Key features of iOS 5:
With iOS 4, the futuristic iOS began to take form as Apple renamed the “iPhone OS” to “iOS” for the first time. Many revisions to this version included features such as FaceTime, multitasking, iBooks, Game Center, organizing programs into folders, custom wallpapers, Personal Hotspot, AirPlay, and AirPrint.
Moreover, Apple included Bing as a search engine for Safari and enabled users to consolidate multiple email accounts into a single inbox. It was the first iteration of iOS to stop supporting all iOS devices. It was incompatible with the first-generation iPod touch or the iPhone.
Key features of iOS 4:
iOS 3 was the first operating system for the iPad and came pre-installed on the iPhone 3GS without any additional charge. Users could copy and paste text system-wide. Besides, Spotlight search, MMS support in the Messages app, and the capability to shoot films using the Camera app are just a few of the new features it includes.
Key features of iOS 3;
iPhone OS 2 was meant for the iPhone 3G model, which included support for the 3G network. As the iPhone became a huge hit, app developers attempted to jailbreak it to install third-party apps. So, Apple introduced development tools like APIs and SDKs for software companies to launch apps in the App Store, thereby preventing the installation of apps from the web.
The App Store had around 500 applications when it debuted. Podcast support, walking and public transportation instructions in Maps, an iTunes Genuine playlist, and enhancements to Mail, Calculator, and Contacts using Microsoft Exchange support were other significant additions to iPhone OS 2.
Key features of iOS 2:
iOS debuted with the release of the first iPhone in June 2007. Nevertheless, it was mostly powered by OS X, the Mac software. It featured a core iOS UI, iTunes integration, Multi-touch gestures, Mobile Safari, iPod, Visual Voicemail, and Maps, which were advanced smartphone capabilities at the time.
However, it lacked support for third-party applications and came with basic pre-installed apps, including Calendar, Pictures, Camera, Notes, Mail, and Phone.
Key features of iOS 1:
From its humble beginnings as iPhone OS to the powerful and intelligent iOS 26, Apple’s mobile operating system has consistently led innovation in the smartphone world. Each update has not only refined the user experience but also anticipated what’s next in mobile technology.
As Apple moves forward with Apple Intelligence, spatial design, and deeper device integration, iOS continues to set the standard for what a modern mobile OS can achieve.
Explore more…